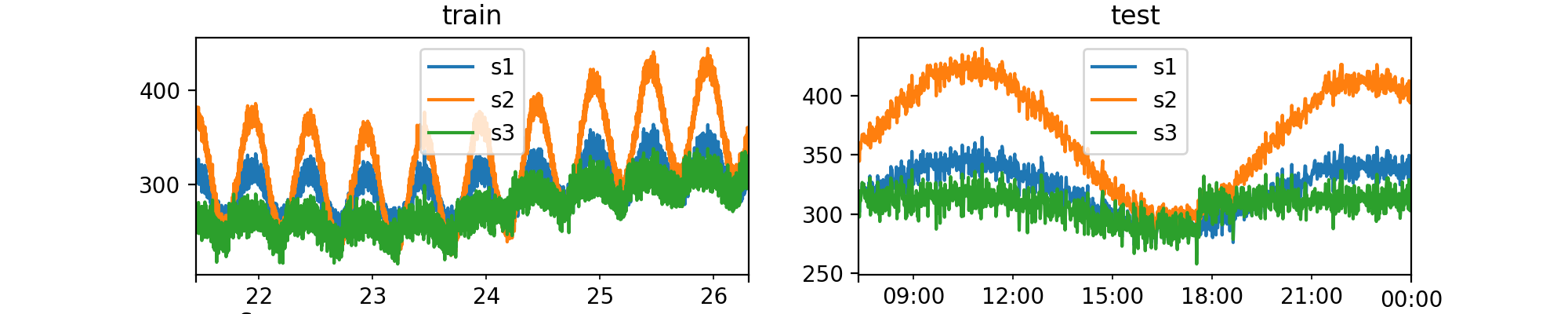
Data Generator¶
Numalogic provides a data generator to create some synthetic time series data, that can be used as train or test data sets.
Using the synthetic data, we can:
- Compare and evaluate different ML algorithms, since we have labeled anomalies
- Understand different types of anomalies, and our models' performance on each of them
- Recreate realtime scenarios
Generate multivariate timeseries¶
from numalogic.synthetic import SyntheticTSGenerator
ts_generator = SyntheticTSGenerator(
seq_len=8000,
num_series=3,
freq="T",
primary_period=720,
secondary_period=6000,
seasonal_ts_prob=0.8,
baseline_range=(200.0, 350.0),
slope_range=(-0.001, 0.01),
amplitude_range=(10, 75),
cosine_ratio_range=(0.5, 0.9),
noise_range=(5, 15),
)
# shape: (8000, 3) with column names [s1, s2, s3]
ts_df = ts_generator.gen_tseries()
# Split into test and train
train_df, test_df = ts_generator.train_test_split(ts_df, test_size=1000)
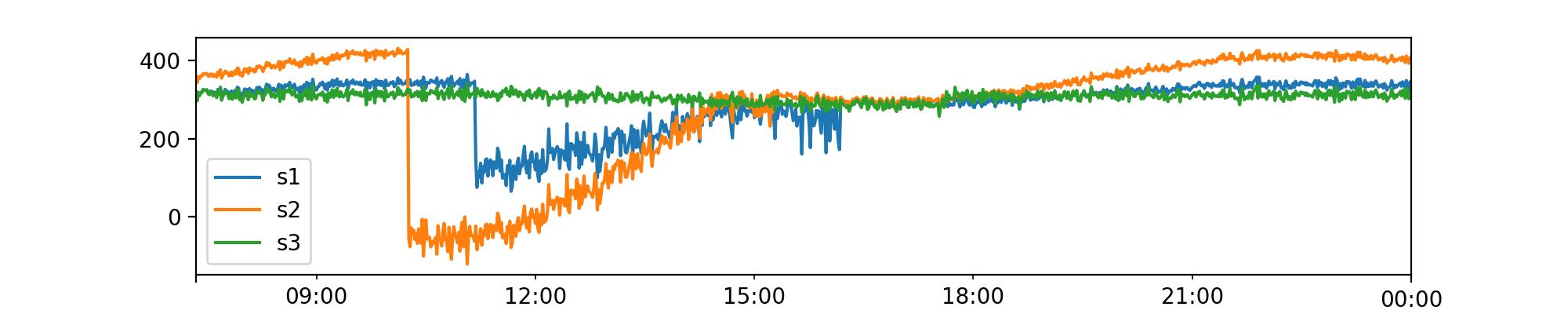
Inject anomalies¶
Now, once we generate the synthetic data like above, we can inject anomalies into the test data set using AnomalyGenerator.
AnomalyGenerator supports the following types of anomalies:
- global: Outliers in the global context
- contextual: Outliers only in the seasonal context
- causal: Outliers caused by a temporal causal effect
- collective: Outliers present simultaneously in two or more time series
You can also use anomaly_ratio to adjust the ratio of anomalous data points wrt number of samples.
from numalogic.synthetic import AnomalyGenerator
# columns to inject anomalies
injected_cols = ["s1", "s2"]
anomaly_generator = AnomalyGenerator(
train_df, anomaly_type="contextual", anomaly_ratio=0.3
)
outlier_test_df = anomaly_generator.inject_anomalies(
test_df, cols=injected_cols, impact=1.5
)